CARs Part 101.01
"control zone" - means the controlled airspace that is so specified in the Designated Airspace Handbook and that extends upwards vertically from the surface of the earth up to and including 3,000 feet AGL, unless otherwise specified in that Handbook
AIM - RAC 2. 7. 3
Control Zones
Control zones are designated around certain aerodromes to keep IFR aircraft
within
controlled airspace during approaches and to facilitate the control of VFR and
IFR
traffic.
Control zones having a civil control tower within a terminal control area
normally
have a 7-NM radius. Others have a 5-NM radius, with the exception of a few which
have a 3-NM radius. Control zones are capped at 3 000 feet AAE unless otherwise
specified. Military control zones usually have a 10-NM radius and are capped at
6 000
feet AAE. All control zones are depicted on VFR aeronautical charts and the
Enroute
Low Altitude Charts.
Control zones will be classified as “B”, “C”, “D” or “E” depending on the
classification of the surrounding airspace.
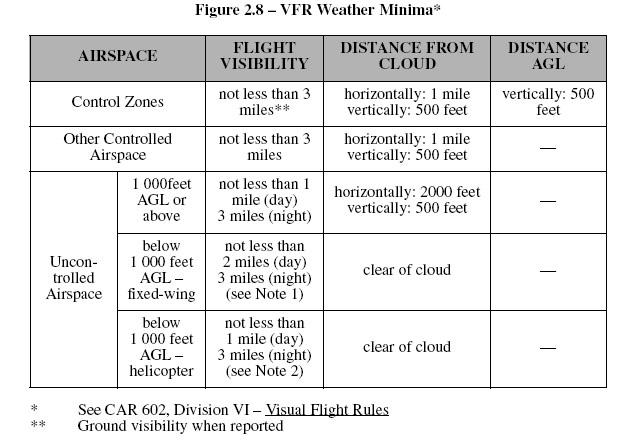
The VFR weather minima for control zones are outlined in Figure 2.8. When
weather
conditions are below VFR minima, a pilot operating VFR may request special VFR
(SVFR) authorization in order to enter the control zone. This authorization is
normally
obtained through the local tower or FSS, and must be obtained before SVFR is
attempted within a control zone. ATC will issue an SVFR authorization, traffic
and
weather conditions permitting, only upon a request for SVFR from a pilot. SVFR
will
not be initiated by ATS. Once having received SVFR authorization, the pilot
continues
to remain responsible for avoiding other aircraft and weather conditions beyond
the
pilot’s own flight capabilities and the capabilities of the aircraft.

NOTES:
1: Notwithstanding CAR 602.115, an aircraft other than an helicopter may
be operated in visibilities less than 2 miles during the day, when
authorized to do so in an air operator certificate or in a private operator
certificate.
2: Notwithstanding CAR 602.115, a helicopter may be operated in
visibilities less than 1 mile during the day, when authorized to do so in
an air operator certificate or in a flight training unit operator certificate -
helicopter.
Special VFR weather minimum and requirements applicable within control zones are
found in CAR 602.117, and are summarized as follows:
Where authorization is obtained from the appropriate ATC unit, a pilot-in-command
may operate an aircraft within a control zone, in IFR weather conditions without
compliance with the IFR, where flight visibility and, when reported, ground visibility
are not less than:
(a) 1 mile for aircraft other than helicopters; and
(b) 1/2 mile for helicopters.
NOTES:1. All aircraft, including helicopters, must be equipped with a radio
capable of communicating with the ATC unit and must comply with all
conditions issued by the ATC unit as part of the SVFR authorization.
2: Aircraft must operate clear of cloud and within sight of the ground at all
times.
3: Helicopters should operate at such reduced airspeeds so as to give the
pilot-in-command adequate opportunity to see other air traffic or
obstructions in time to avoid a collision.
4: When the aircraft is being operated at night, ATC will only authorize
special VFR where the authorization is for the purpose of allowing the
aircraft to land at the destination aerodrome.
